Atopic Dermatitis: Infected - Impetigo (Staph. aureus)
- Can be bullous (bullae forming) or non-bullous impetigo.
- Often from secondary scratching.
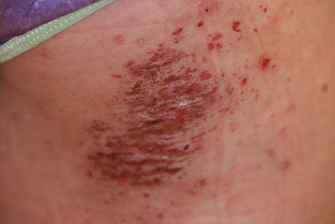
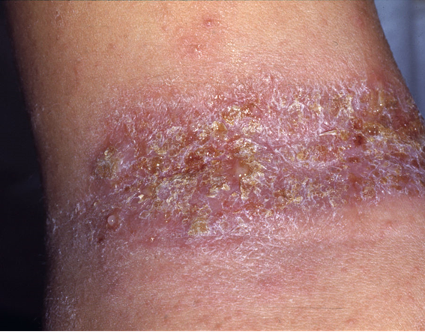
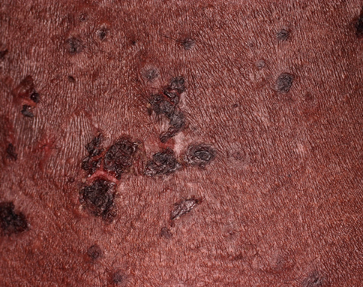
- Non-bullous impetigo: yellow, honey-colored crusting usually within areas of eczema. Typically caused by Staph aureus methicillin sensitive (MSSA), methicillin resistant (MRSA), or group A strep.
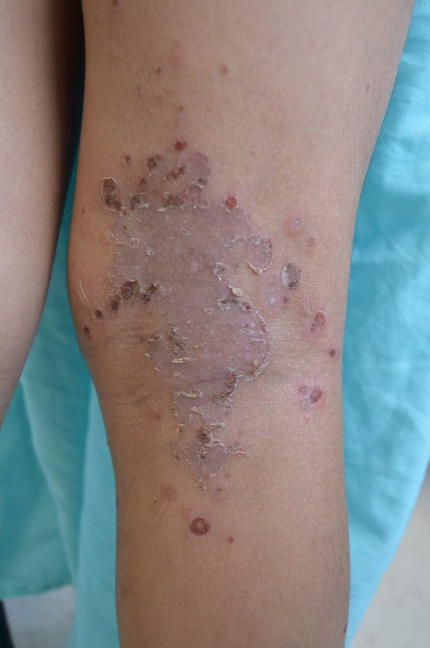
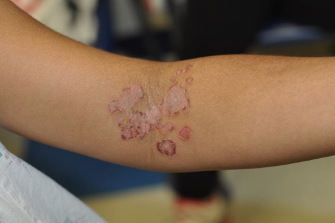
- Bullous impetigo initially presents as thin-walled bullae which quickly rupture (often before seeking medical care) and appear as red annular areas with a fine white collarette of scaling on border of lesions.
- Rapidly spreads within areas of eczema and to other areas of body.
Non-Bullous Impetigo examples follow:
Bullous Impetigo (note fine peripheral scaling) examples follow:
These pathways do not establish a standard of care to be followed in every case. It is recognized that each case is different, and those individuals involved in providing health care are expected to use their judgment in determining what is in the best interests of the patient based on the circumstances existing at the time. It is impossible to anticipate all possible situations that may exist and to prepare a pathway for each. Accordingly, these pathways should guide care with the understanding that departures from them may be required at times.