How a Healthy Heart Works
Sometimes, it’s easier to understand how your child’s heart is different if you have a clearer picture of how a healthy heart works. Learn the basics of the heart’s structure and function from the experts at the Heart Center.
Function of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ. Its job is to pump blood throughout the body. The heart, together with blood vessels, make up the cardiovascular system.
Structure of the heart
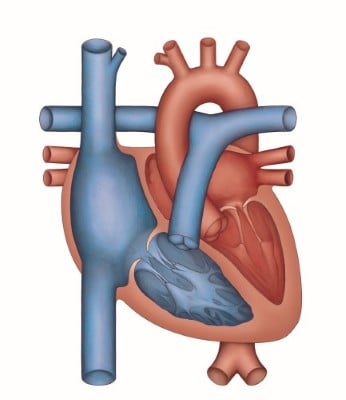
The heart has four chambers, two in the upper half and two in the lower half. The upper chambers are called atria. The lower chambers are called ventricles. The muscular walls that divide the atria and ventricles are called septum.
The right atrium and right ventricle pump oxygen-poor (blue) blood to the lungs. The left atrium and ventricle pump oxygen-rich (red) blood to the body.
There are four valves inside the heart. The valves open and close keeping the blood moving forward through the heart. The tricuspid valve is in between the right atrium and right ventricle. The pulmonary valve is between the right ventricle and the lungs. The mitral valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle. The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Circulation of blood
Blood carries oxygen to the tissues of the body so they can do their job. The blood is delivered from the heart which acts as a pump. The heart also delivers the blood to the lungs where the blood is refilled with oxygen.
Oxygen poor (Blue) blood flows back from the body through the inferior and superior vena cava (big veins coming up from below the heart and down from above the heart), to the right atrium. The atrium empties the blood through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle. The right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary valve, to the pulmonary artery, and into the lungs.
In the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and then is returned to the heart via the pulmonary veins. The pulmonary veins empty into the left atrium. The left atrium sends blood through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps blood through the aortic valve, into the aorta. From the aorta, the blood goes out to the arteries that supply oxygen to the heart and then to the brain and the rest of the body.
Heart beats
Normal heart beats happen when an electrical signal is sent from the sinoatrial (SA) node at the top of the heart then through the atrioventricular (AV) node which is near the tricuspid valve. This electrical impulse spreads across the heart through the Purkinje fibers. The electrical signal causes the heart to contract. When the heart contracts, blood is pumped to the lungs and the rest of the body

Heart care at Children’s Mercy
Our nationally-ranked Heart Center cares for children with all kinds of heart conditions. Learn more about our comprehensive care and how we can help your child.