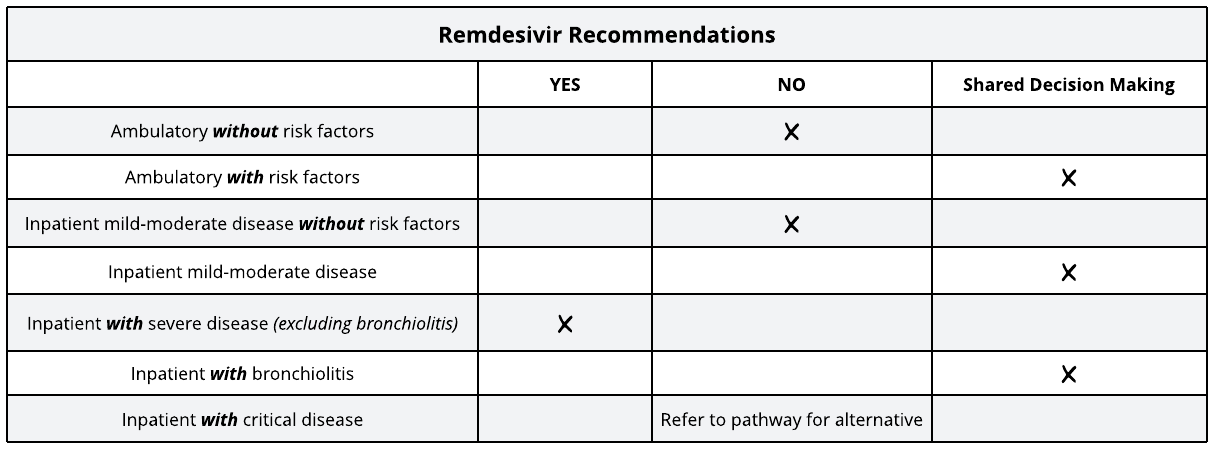
Remdesivir for Children with COVID-19
Is remdesivir effective?
Is remdesivir safe?
|
|
References: Ahmed, A., Munoz, F.M., Muller, W.J., Agwu, A., Kimberlin, D.W., Galli, L., Deville, J.G., Sue, P.K., Mendez-Echevarria, A., Humeniuk, R., Guo, S., Rodriguez, L., Han, D., Hedskog, C., Maxwell, H., Palaparthy, R., Kersey, K., & Rojo, P. (2024). Remdesivir for COVID-19 in hospitalized children: A phase 2/3 study. Pediatrics, 153(3), e2023063775. doi:10.1542/peds.2023-063775 Bhimraj, A., Morgan, R.L., Hirsch Shumaker, A., Baden, L.R., Chi-Chung Cheng, V., Edwards, K.M., Gallagher, J.C., Gandhi, R.T., Muller, W.J., Nakamura, M.M. O’Horo, J.C., Shafer, R.W., Shoham, S., Murad, M.H., Mustafa, R. A., Sultan, S., & Falck-Ytter, Y. (2024, June). Infectious Diseases Society of America: Guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19, Clinical Infectious Diseases, 78(7), e250-e349. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac724 Goldman, J. D., Lye, D. C. B., Hui, D. S., Marks, K. M., Bruno, R., Montejano, R., Spinner, C. D., Galli, M., Ahn, M. Y., Nahass, R. G., Chen, Y. S., SenGupta, D., Hyland, R. H., Osinusi, A. O., Cao, H., Blair, C., Wei, X., Gaggar, A., Brainard, D. M., Towner, W. J., … GS-US-540-5773 Investigators (2020). Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe COVID-19. The New England journal of medicine, 383(19), 1827–1837. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2015301 Goldman, D. L., Aldrich, M. L., Hagmann, S. H. F., Bamford, A., Camacho-Gonzalez, A., Lapadula, G., Lee, P., Bonfanti, P., Carter, C. C., Zhao, Y., Telep, L., Pikora, C., Naik, S., Marshall, N., Katsarolis, I., Das, M., DeZure, A., Desai, P., Cao, H., Chokkalingam, A. P., … Méndez-Echevarría, A. (2021). Compassionate use of remdesivir in children with severe COVID-19. Pediatrics, 147(5), e2020047803. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-047803 Gottlieb, R. L., Vaca, C. E., Paredes, R., Mera, J., Webb, B. J., Perez, G., Oguchi, G., Ryan, P., Nielsen, B. U., Brown, M., Hidalgo, A., Sachdeva, Y., Mittal, S., Osiyemi, O., Skarbinski, J., Juneja, K., Hyland, R. H., Osinusi, A., Chen, S., Camus, G., … GS-US-540-9012 (PINETREE) Investigators (2022). Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. The New England journal of medicine, 386(4), 305–315. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116846 Jinda, T., Mizuno, S., Tatami, S., Kasai, M., & Ishida, T. (2024). Risk factors for liver enzyme elevation with remdesivir use in the treatment of paediatric COVID-19. J Paediatr Child Health, 60(7), 299–302. doi:10.1111/jpc.16569 Kautsch, K., Wiśniowska, J., Friedman-Gruszczyńska, J., & Buda, P. (2024). Evaluation of the safety profile and therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection - a single-center, retrospective, cohort study. Eur J Pediatr, 183(2), 591-598. doi:10.1007/s00431-023-05287-4 Manabe, S., Mizuno, S., Jinda, T., & Kasai, M. (2022). Safety of remdesivir in 20 children with COVID-19-case series-Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 45(12), 1853–1856. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b22-00470 Minotti, C., Mengato, D., De Pieri, M., Trivellato, S., Francavilla, A., Di Chiara, C., Liberati, C., Mattera, R., Biffi, A., Giaquinto, C., Venturini, F., & Donà, D. (2023). Early treatments of fragile children with COVID-19: Results of CLEVER (Children COVID Early Treatment), a retrospective, observational study. Viruses, 15(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010192 Player, b., Huppler, A.R., Pan, A.Y., Liegl, M., Havens, P.L., Ray, K., Mitchell, M., & Graff, K. (2024). Safety of remdesivir in the treatment of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection in pediatric patients. BMC Infectious Diseases, 24, 987. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-024-09833-9 Romani, L., Roversi, M., Bernardi, S., Venturini, E., Garazzino, S., Donà, D., Krzysztofiak, A., Montagnani, C., Funiciello, E., Calò Carducci, F. I., Marabotto, C., Castagnola, E., Salvini, F., Lancella, L., Lo Vecchio, A., Galli, L., Castelli Gattinara, G., & Italian Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases (SITIP) (2024). Use of remdesivir in children with COVID-19: Report of an Italian multicenter study. Italian journal of pediatrics, 50(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13052-024-01606-z Samuel, A. M., Hacker, L. L., Zebracki, J., Bogenschutz, M. C., Schulz, L., Strayer, J., Vanderloo, J. P., Cengiz, P., & Henderson, S. (2023). Remdesivir use in pediatric patients for SARS-CoV-2 treatment: Single academic center study. The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal, 42(4), 310–314. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000003814 Shoji, K., Asai, Y., Akiyama, T., Tsuzuki, S., Matsunaga, N., Suzuki, S., Iwamoto, N., Funaki, T., Miyairi, I., & Ohmagari, N. (2023). Clinical efficacy of remdesivir for COVID-19 in children: A propensity-score-matched analysis. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy: Official Journal of the Japan Society of Chemotherapy, 29(9), 930–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2023.06.006 Spinner, C. D., Gottlieb, R. L., Criner, G. J., Arribas López, J. R., Cattelan, A. M., Soriano Viladomiu, A., Ogbuagu, O., Malhotra, P., Mullane, K. M., Castagna, A., Chai, L. Y. A., Roestenberg, M., Tsang, O. T. Y., Bernasconi, E., Le Turnier, P., Chang, S. C., SenGupta, D., Hyland, R. H., Osinusi, A. O., Cao, H., … GS-US-540-5774 Investigators (2020). Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 Days in patients with moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 324(11), 1048–1057. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.16349 |
These pathways do not establish a standard of care to be followed in every case. It is recognized that each case is different, and those individuals involved in providing health care are expected to use their judgment in determining what is in the best interests of the patient based on the circumstances existing at the time. It is impossible to anticipate all possible situations that may exist and to prepare a pathway for each. Accordingly, these pathways should guide care with the understanding that departures from them may be required at times.